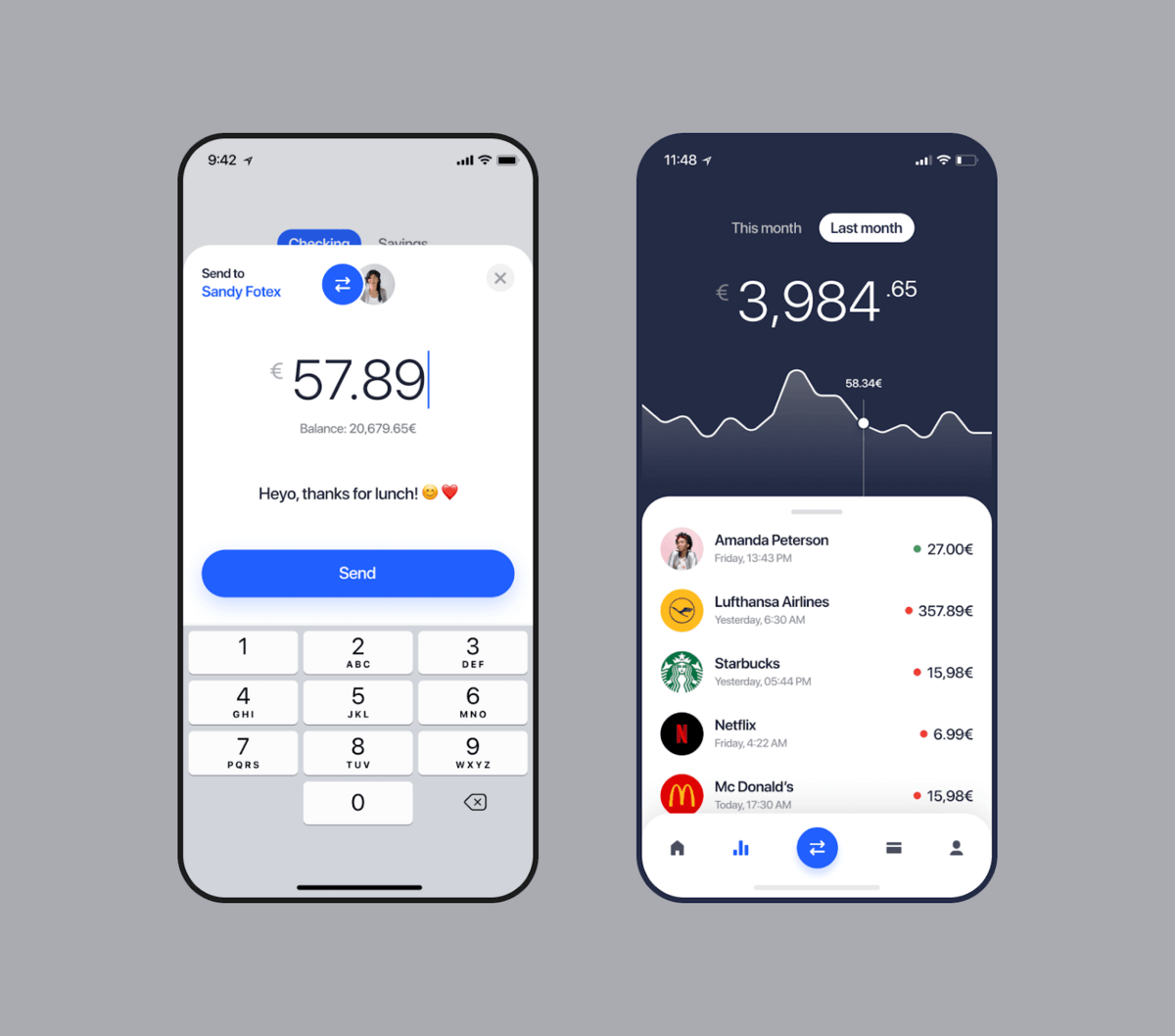
Mobile wallets are by far one of the most profitable fintech niches, thanks to a huge surge in digital payments during the pandemic.
And their popularity is only going to continue to grow. Juniper Research revealed that the number of digital wallet users is likely to increase to 4.4 billion in 2025, from 2.6 billion in 2020.
Mobile wallet apps are at the forefront of this growth, making it a lucrative niche for anyone wanting to enter fintech. However, it is also very competitive, as the sector is dominated by big players such as Apple and Google.
To succeed, your mobile wallet app needs to get the basics right first. Here’s a rundown of the fundamentals.
What is a mobile wallet app and how does it work?
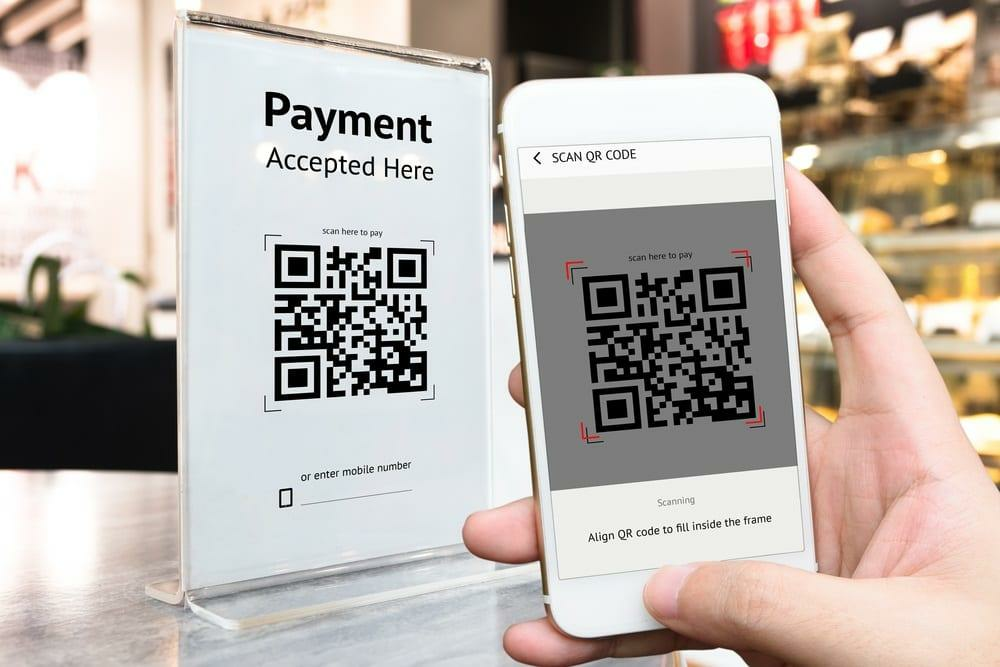
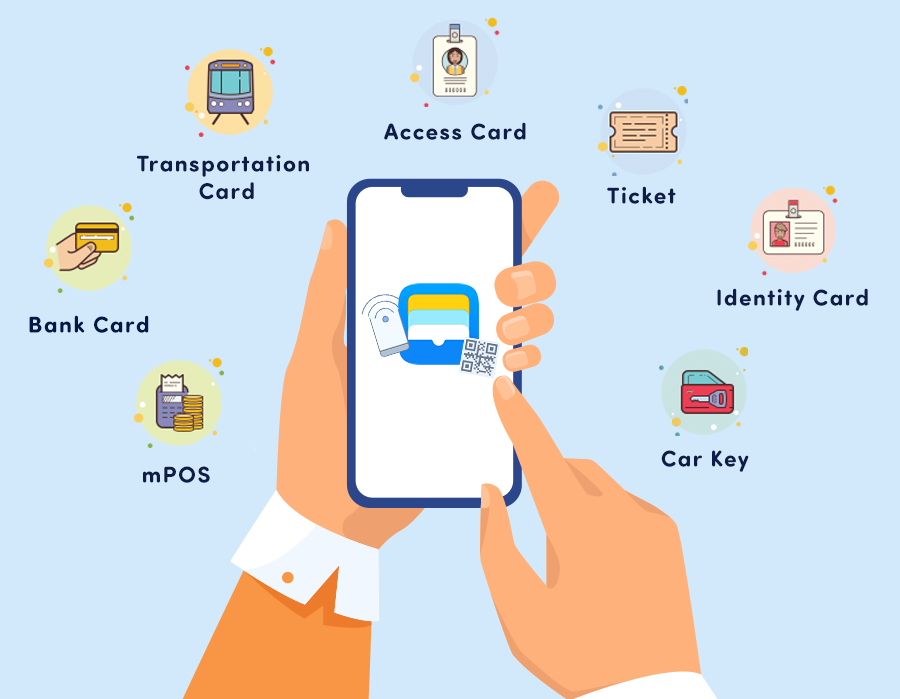
The name is already pretty self-explanatory—a mobile wallet is an app where you can store your payment information, allowing you to send payments from your smartphone, both online and offline.
But payments are just the beginning. Just like real wallets, you can easily store and access your discount cards, loyalty cards, bus tickets—even your car keys.
Source: Xpress Money
In essence, mobile wallets are apps that keep your private data safe. But it doesn’t end there—they can also send your data securely to a third-party merchant or retailer when necessary.
This can be done in various ways, from QR codes to near-field communication (NFC). All the user needs to do is place their phone near a reader to initiate the transaction.
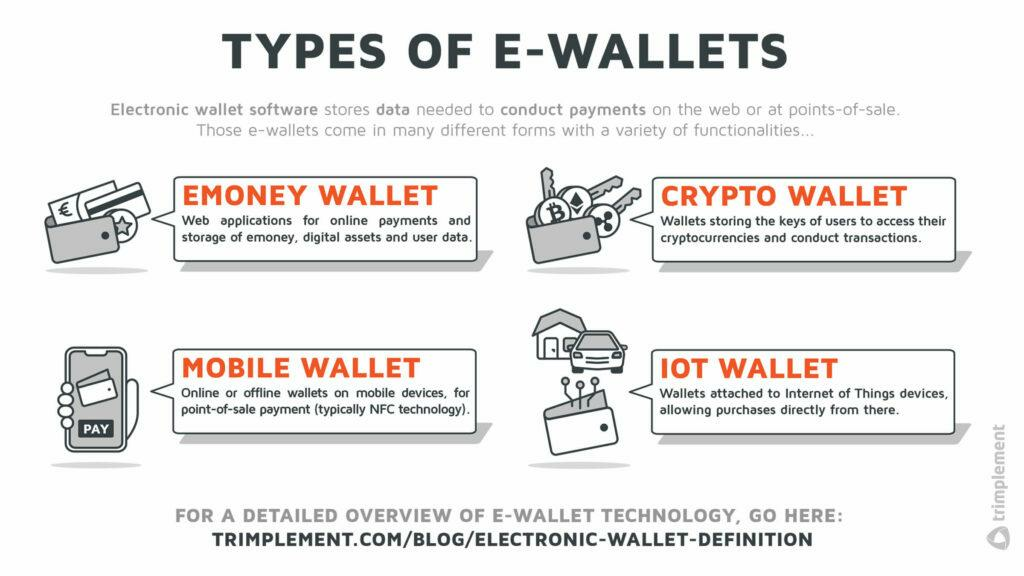
Many people fail to distinguish digital wallets from mobile wallets. While they both have the same purpose, there are some important differences between the two.
There are various kinds of electronic wallets. Mobile wallets are just one of them.
Source: Trimplement
So, what’s the difference?
Digital wallets are a much broader category and denote any electronic wallet that stores payment information. They’re often web-based and are used primarily for online payments and the storage of financial assets.
On the other hand, the term mobile wallets is specific to electronic wallets installed on a smartphone.
On top of what digital wallets can do, the mobile ones are designed to also work with retail merchants through contactless readers. Some even allow you to pay while offline.
Mobile wallets themselves have various subtypes. We’ll discuss these next.
What are the different types of mobile wallet apps?
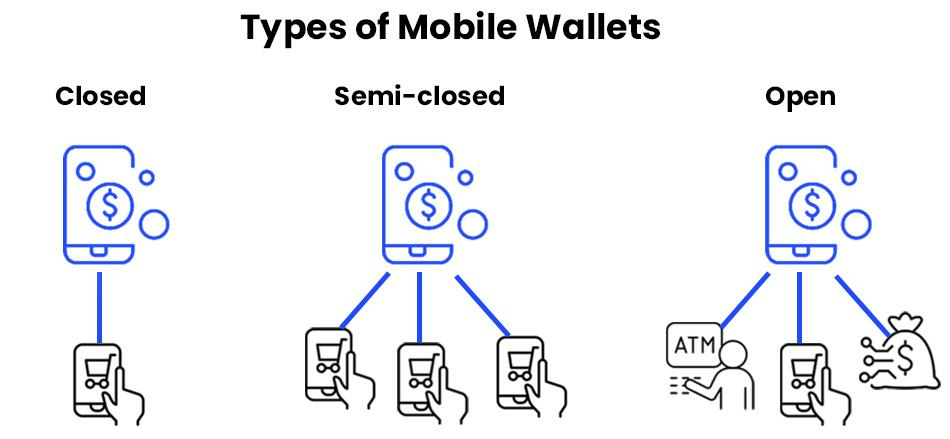
Mobile wallets can be classified into three types: closed, semi-closed, and open.
Source: DECODE
Let’s describe each kind in more detail.
Closed wallets
Closed wallets are issued by a specific company and can only be used for transactions involving it or accredited merchants. A good example of a closed wallet is Amazon Pay.
While customers can use it on various websites, everything is still coursed through your Amazon account.
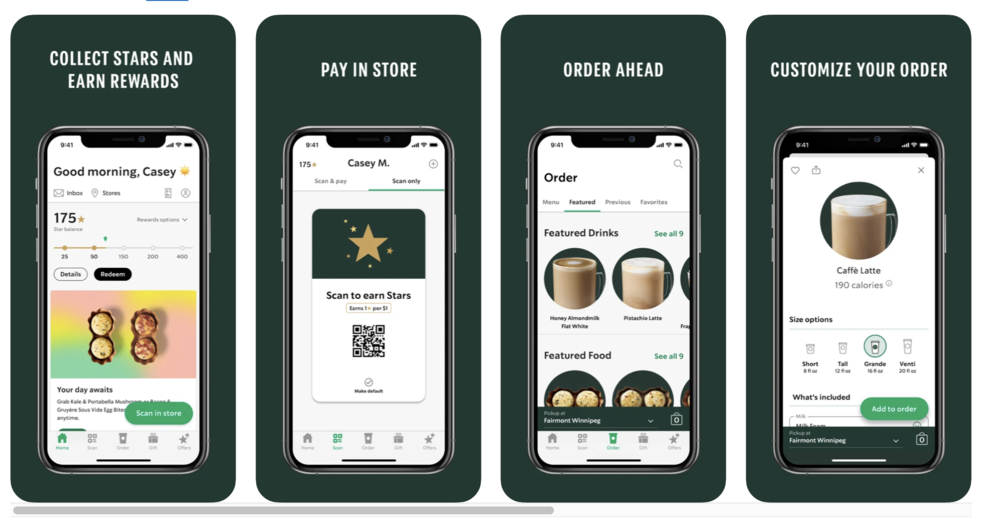
While closed wallets are restrictive from a customers’ point of view, they’re fantastic from a loyalty standpoint. For example, the Starbucks app allows users to pay for their drinks at their branches and earn rewards points in the process.
Source: Starbucks
Closed wallets are also cheaper since they don’t involve merchant fees. They can also offer a wealth of data on a person’s spending habits and behavior.
Semi-closed wallets
Semi-closed walletsallow users to send payments to any merchant, as long as they have an existing agreement with the wallet’s payment provider.
In addition, people can also send payments to other wallet users within the network and use other financial services. Non-banking institutions often offer them with the approval of a partner bank.
This type of mobile wallet is arguably the most widely available, as it’s much more flexible than a closed wallet. For users, it’s also convenient since they can make all of their payments in just one app.
Source: Venmo
However, semi-closed wallets are less than ideal from the merchant’s perspective. It’s hard to implement loyalty programs with them, and merchants don’t have access to consumer data.
Good examples of semi-closed wallets are Apple Pay and Venmo.
Open wallets
Open walletsare similar to semi-closed wallets and have their own pros and cons. However, a key distinction is that open wallets also allow users to withdraw cash from an ATM.
A perfect example is Paypal. Apart from letting you send money and make payments, it also allows you to withdraw cash from banks or through an ATM.
Some digital banks also offer mobile wallets, but it’s often implemented as a banking app feature and not a standalone platform.
Why are mobile wallet apps popular?
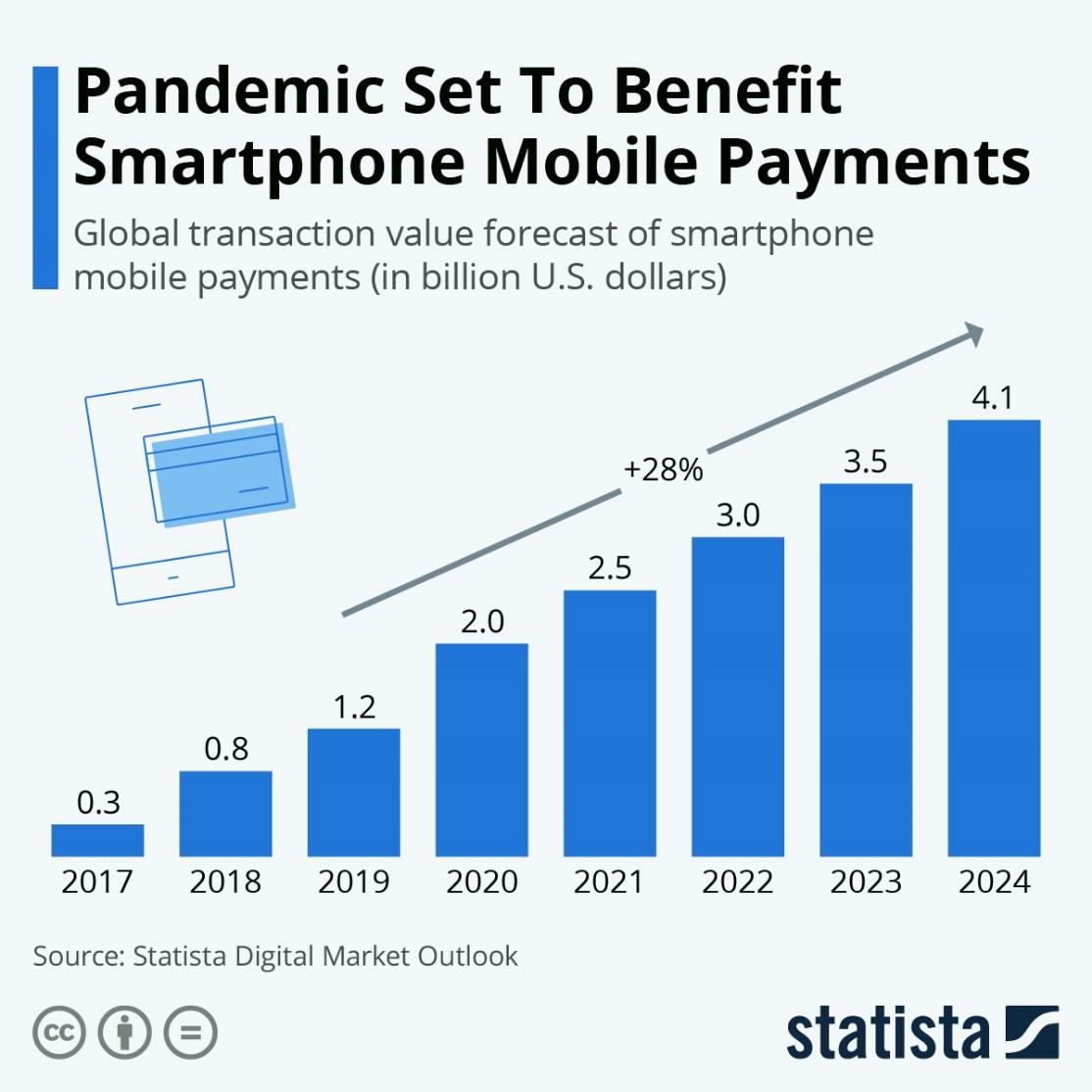
As mentioned in the introduction, the mobile wallet niche is one of the fastest-growing ones in fintech. The market was valued at $101.2 billion in 2020, and it’s projected to soar to $750.3 billion by 2028—a massive 700% growth in less than a decade.
This market performance has been accelerated mostly during the COVID-19 pandemic. You can see it clearly in this Statista prediction.
Source: Statista
This sharp increase is understandable since social distancing and lockdowns meant people relied more on online transactions.
But even with the pandemic losing steam in most countries, it’s expected that mobile wallet usage will continue to enjoy remarkable growth.
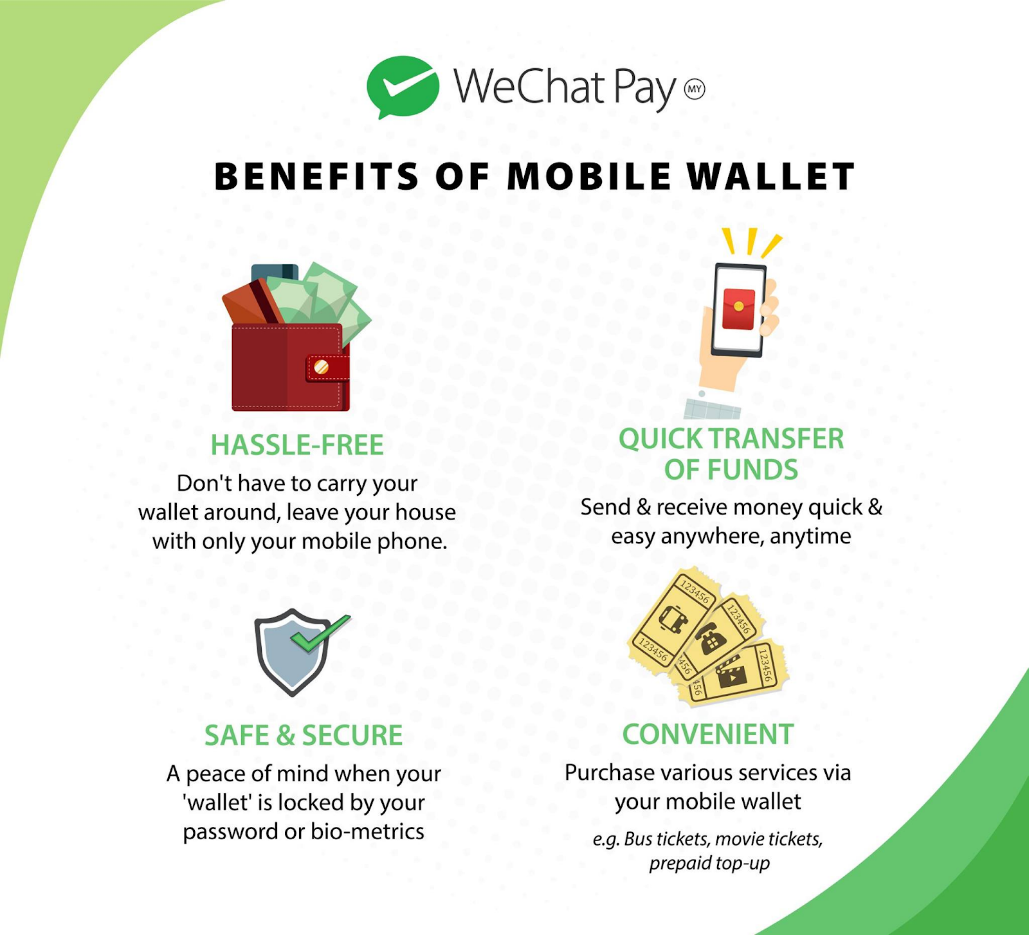
The reason? Mobile wallets have so many benefits that it’s hard to go back to relying on older payment methods.
Source: SciComm
One of the key benefits is safety. Compared to physical wallets or even web-based e-wallets, mobile wallets are harder to steal. In addition, most apps have multiple layers of security, including biometrics, encryption, and multi-factor authentication (MFA).
Such security means mobile wallets are much more challenging to hack. Even if a thief managed to steal a person’s smartphone, bypassing biometrics is not a trivial task. Plus, wallet data is encrypted.
And since mobile wallets are contactless, in the pandemic, the benefits extend to your health and physical safety too.
The other big benefit is convenience. With mobile wallets, you don’t need to carry around a physical wallet with all of your cards in it. You can also complete transactions in seconds with a simple tap of your phone.
No doubt you’re already contemplating getting into the mobile wallet market. But for your app to stand out, it needs a few critical features. So let’s look into what they are.
Key features to include
Mobile wallets are more than just sending or receiving money. To stand out, it needs a host of support features to achieve a seamless and efficient experience for the user.
Arguably, your app lives and dies by the number of payment channels it supports—the more, the better.
Try to integrate your mobile wallet with every major POS or terminal for the best flexibility. Users should be able to pay their bills, send money to other wallet users, or pay for financial services like insurance.
Also, consider the storage of non-financial data such as transportation tickets and hotel keys, a good practice held by Huawei Pay, among others.
Source: The Paypers
Adding payment information needs to be as seamless and painless as possible. At the minimum, your wallet should support linking a user’s bank account.
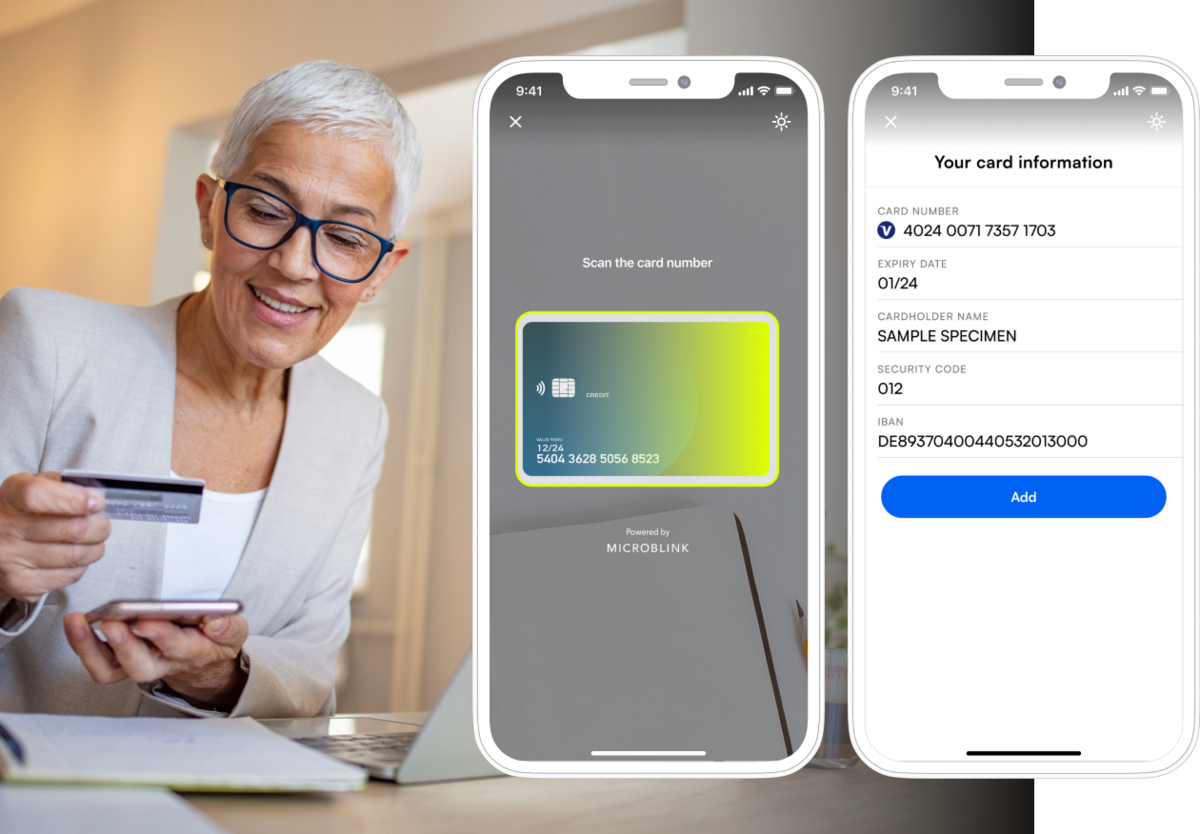
Card scanning, which automatically reads card details through a camera, is always a good idea. This eliminates the need for manual entry, which is both tedious and can lead to errors, especially when multiple credit cards are involved.
Of course, it’s also easy to implement these in your app with APIs such as Microblink.
Source: Microblink
Tracking and analytics are also important features. You want users to be able to review and monitor their transactions, both to manage their habits, or to ensure safety when something goes wrong.
Of course, don’t forget about UX features like customizable push notifications and easy-to-use UI.
For more advanced features, you can incorporate a loyalty program into your mobile wallet app. You can either devise your own, or partner with select merchants.
Of course, you can do the same with gift cards as well. Plus, integrating with things like the cloud and wearable tech can future-proof your app.
Lastly, you should provide multiple contactless payment options. That involves using mobile data transfer technologies, which we’ll explore next.
Data transfer technologies for mobile wallets
Currently, there are three primary data transfer technologies used by mobile wallets.
QR codes are the most popular. This technology involves a user scanning a merchant’s unique QR code to initiate a payment transaction. They then specify the amount, which is automatically credited to the merchant.
Source: Pymnts.com
The reason behind the wide acceptance of QR codes lies in their simplicity. They also don’t require any special device or technology— all you need is a camera, which every modern smartphone has.
However, research shows that QR codes are slowly waning in popularity. By 2025, QR codes will account for only 40% of wallet transactions, which is a big decline from 47% in 2020. This is due to the influx of more advanced technologies, such as NFC.
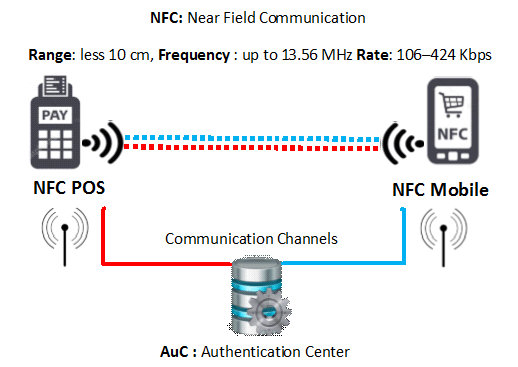
NFC, or Near Field Communication, is a technology that facilitates data transfer through NFC chips. It sends small data using radio waves whenever two devices are closed to one another.
Here’s an illustration of how it works.
Source: Shadi Nashwan via ResearchGate
NFC is more convenient and faster than QR codes because you only need to place your smartphone near a terminal to initiate a transaction. It’s also much more secure.
However, since NFC isn’t as widespread yet, QR codes are still the primary way of sending payments.
But that could change soon. NFC is gaining more popularity, and current wallets that support this technology include Apple Pay and Google Pay.
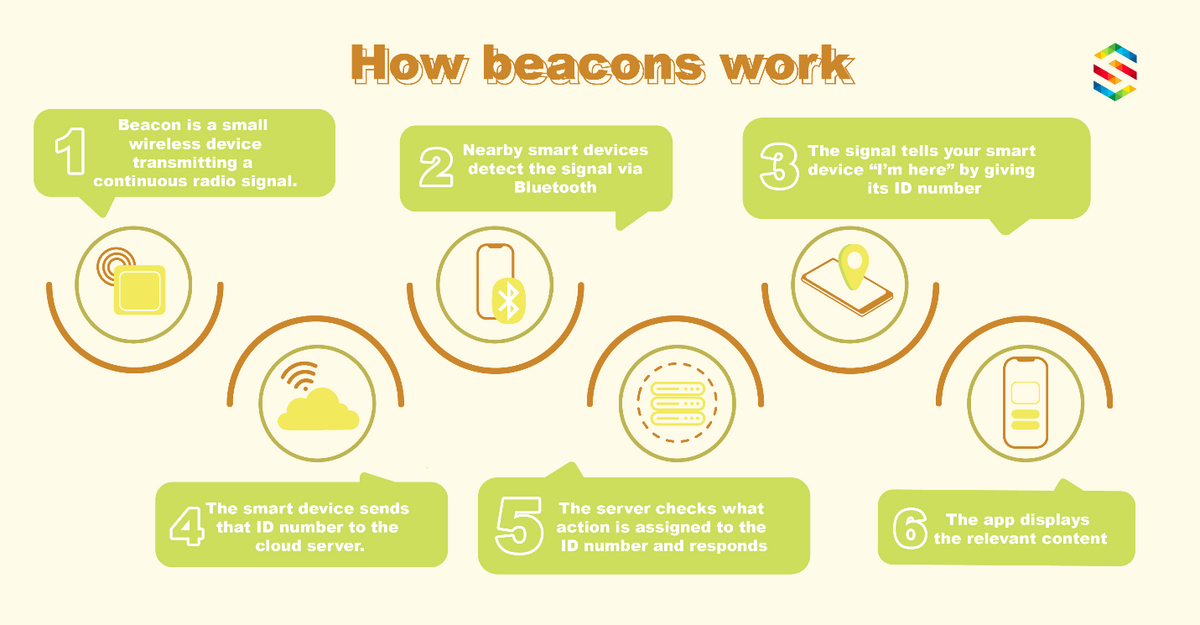
Finally, let’s look at iBeacon, which relies on Bluetooth technology and works roughly the same way. Like NFC, it allows smartphones and readers (called beacons) to communicate without an internet connection.
Source: Softensy
The main advantage of iBeacon is that it covers a wider area. That means a user can be anywhere in a store and still connect to a store’s POS terminal. However, the biggest drawback of this technology is that it requires a considerable investment.
The bottom line is that these data transfer technologies have their uses, depending on the situation. An important consideration, though, is how secure they are. This brings us to our next topic.
Security technologies used for a mobile wallet app
Security is by far the most critical aspect of a mobile wallet as they’re incredibly attractive targets for hackers. Indeed, a report by the cyber security firm Cognyte discovered rampant selling of Apple Pay and Google Pay vulnerabilities on the dark web.
Luckily, mobile wallets have more security layers than a typical wallet.
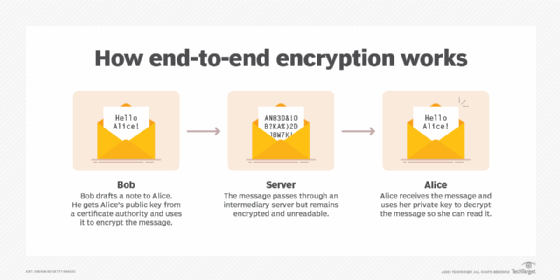
Point-to-point encryption is one of the most fundamental of these technologies. It involves garbling your wallet data to make it useless to hackers.
The only time the data gets unencrypted is during payment authorization, before it is sent to the payment processor.
Source: Tech Target
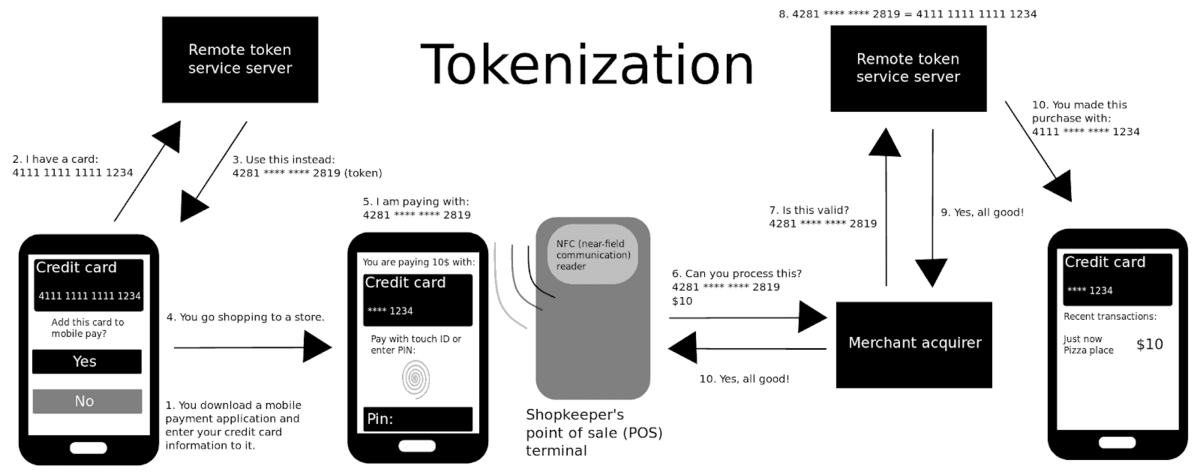
Next, tokenization is a security protocol similar to encryption: you convert sensitive financial information like a credit card number into a random number called a token. You then use this token instead of your card number when sending transactions.
Here’s a handy diagram.
Source: Wikipedia
Lastly, there’s the old method of using passwords. Though relatively unreliable, they still provide a level of protection as long as they’re used properly.
You can enhance the strength of your passwords by adding additional protocols like biometrics and MFA to authorize transactions.
At the end of the day, security isn’t about picking the best security protocol among those mentioned above. Rather, it’s best to combine these methods to build an impenetrable shield against hackers.
Programming languages and SDKs for mobile wallet apps
Your tech stack forms a very important aspect of fintech app development. But in mobile wallets, two stand out: the programming language and the SDK.
When it comes to your language of choice, a few stand out.
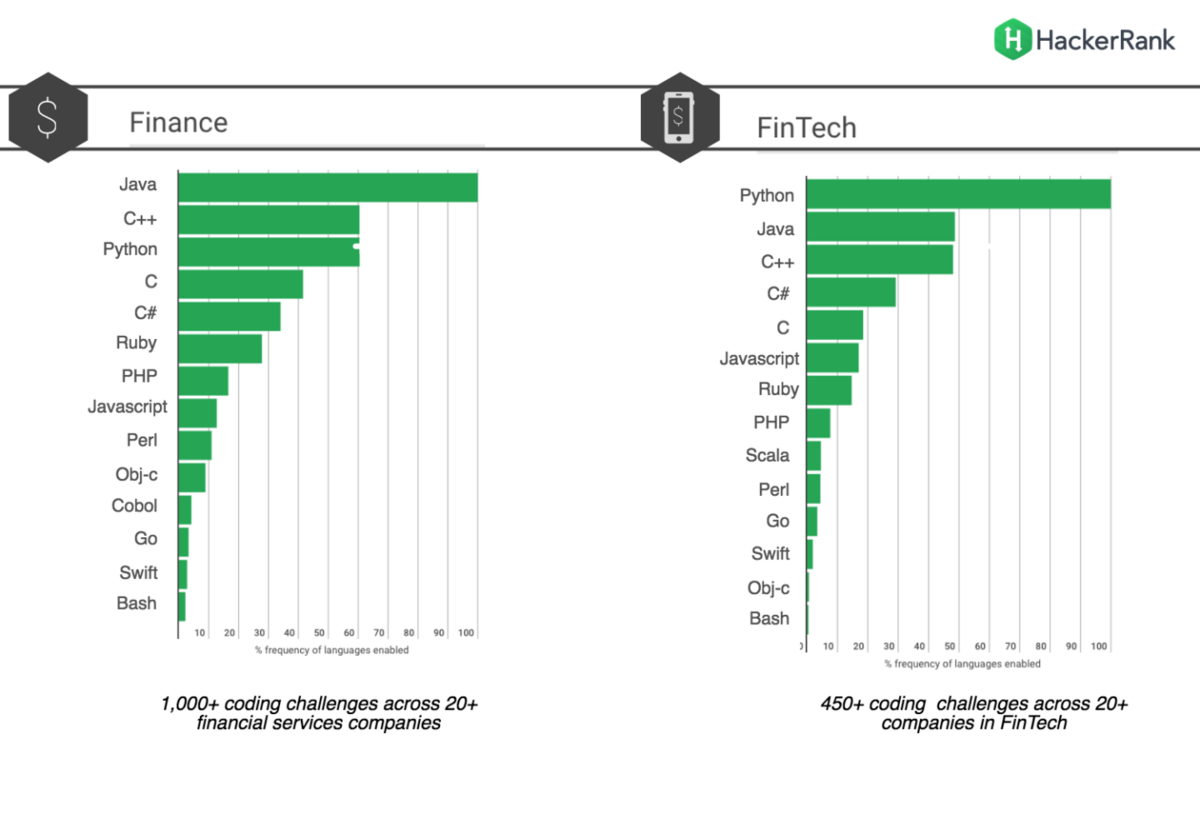
Python and Java remain the most popular choices for coding the backend of your wallet app, thanks to their speed and security. Scala is also gaining popularity. And while C++ is useful for complex calculations, it’s unlikely you’ll encounter it in a mobile wallet app.
Source: The Codest
For the app itself, performance speed is essential, so it’s best to stick with native languages like Swift for iOS and Kotlin for Android. If you absolutely have to go hybrid, React Native is a good pick.
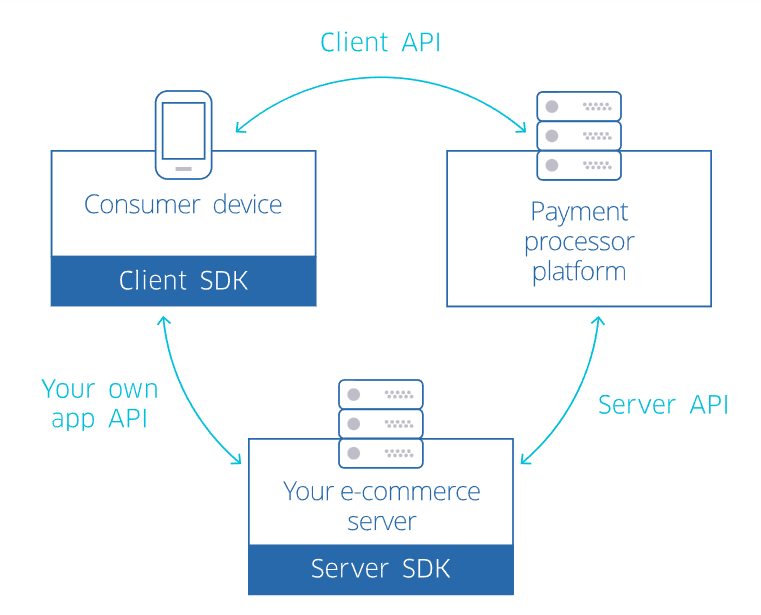
The other important ingredient for mobile wallet development is mobile payment SDK. SDKs, or Software Development Kits, are the specific software libraries that you use to integrate a particular platform or API into your app—in this case, payment gateways.
You’ll need to incorporate their SDKs into your development for every payment gateway you want to use in your app.
For example, if you’re going to accept Mastercard transactions, you need the Mastercard Mobile Payment (MCBP) SDK. The same is true for platforms like Paypal, Stripe, and Visa.
Here’s an example of how an SDK works to make secure payments using the Worldline platform.
Source: Worldline
SDKs are often straightforward to use, and they allow you to tap into popular payment channels on your app. However, make sure to review the rules and regulations before implementing them.
Examples of popular mobile wallet apps
As we mentioned, the mobile wallet niche is an incredibly popular one. So, it’s no surprise that it’s filled with lots of excellent app examples, built by everyone from independent developers to the world’s biggest tech firms.
In fact, most smartphones today likely have a mobile wallet app already pre-installed. For instance, iPhones use the Wallet app to make payments using Apple Pay.
Moreover, as a native Apple app, it benefits from iPhone features like Siri support and secure Face ID authentication.
Source: Apple
Similarly, Android users have access to Google Pay by default. It has the same features like Apple Pay, including sending cash to other people. Both also have wide support from major credit cards and establishments.
Source: Google
Apart from these two, there are also other third-party apps you can consider. For example, Venmo is incredibly popular these days thanks to the ease of sending money to individuals it offers, including via email or phone number.
However, it has relatively limited acceptance in retail stores, making this more useful as a peer-to-peer payment app.
Source: Venmo
As for closed wallets, many large retailers offer them as part of their digital marketing offerings. One of those retailers is Walmart. Their Walmart Pay app allows customers to pay using QR codes at Walmart stores. It’s also an easy way to organize and use gift cards.
On the other hand, Vodafone M-PESA is one of the more successful examples of an open wallet. It’s a mobile money service deployed primarily in Africa.
Beyond payment, users can withdraw money, make loans, pay bills, and even invest in financial instruments through the app.
No wonder M-PESA is Africa’s largest fintech platform, handling an incredible $314 billion worth of transactions annually.
Source: AppAgg
As our last example, let’s look at a project that DECODE did with Asseco SEE, one of the top fintech software providers in Europe. We were asked to enhance one of their mobile banking apps—with a mobile wallet as the key feature.
Source: DECODE
You can read the case study here if you’re interested.
This is just the tip of the iceberg that is the mobile wallet market. There are many other independent or region-specific apps (such as Alipay in China). So there’s no danger of you running out of inspiration for your project.
Ready to build your mobile wallet app?
No doubt you’ve seen the potential of the mobile wallet market. And while it’s highly competitive, standing out isn’t impossible. You just need the right features and an experienced agency partner to guide you.
And we’re ready to help! So contact us today, and let’s start bringing your idea to life.